News

January 20, 2026
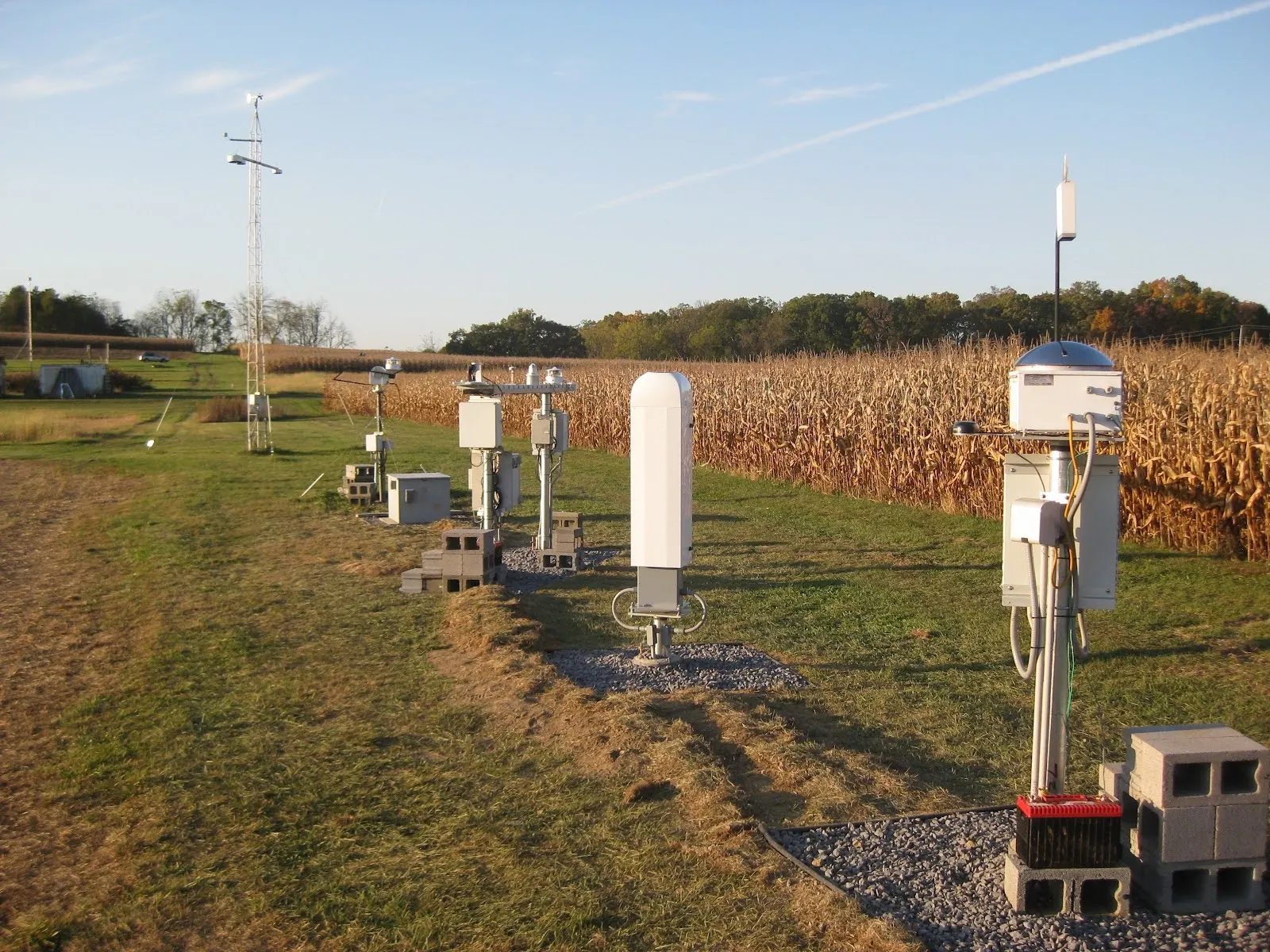
GML team installed meteorological instruments at the Colorado Atmospheric Observatory tower
On January 15, staff from the Global Monitoring Laboratory’s (GML) Observatory and Global Network Operations division completed installation of meteorological (MET) instruments at the lab’s Colorado Atmospheric Observatory tower in Byers, CO.January 20, 2026
GML highlights at the 2026 AMS annual meeting
GML and CIRES researchers and GML summer interns are presenting several talks and posters, and collaborating on others, at the 2026 annual meeting of the American Meteorological Society.December 22, 2025
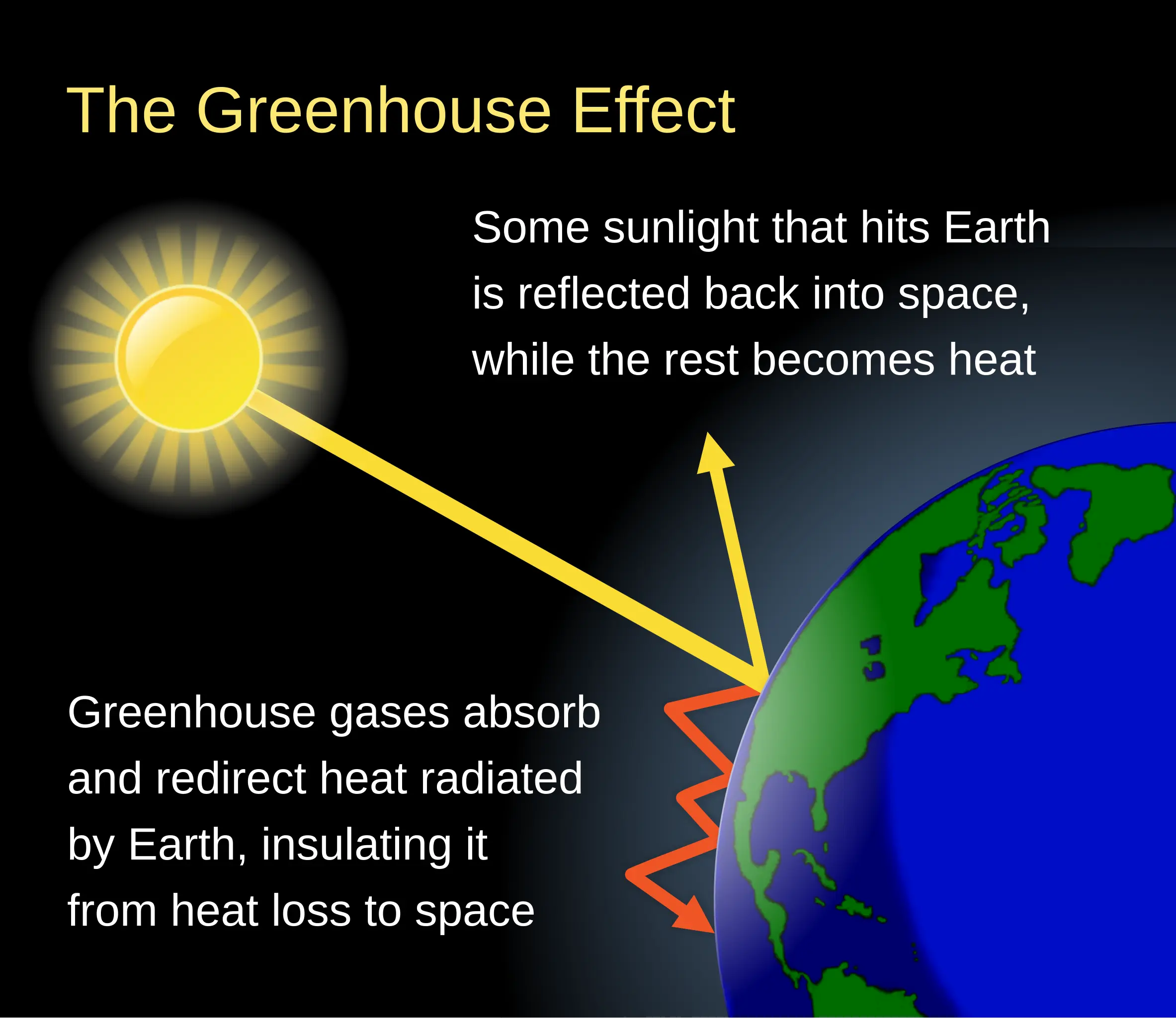
NOAA index tracks the continuing increase in heating from greenhouse gases
Greenhouse gases associated with human activity trapped 54 percent more heat in the atmosphere during 2024 than those same gases did in 1990, according to an annual NOAA report.December 18, 2025
International report chronicles atmospheric impacts of 2022 Hunga volcanic eruption
A report released today by the World Climate Research Programme provides a comprehensive analysis of the atmospheric effects of the January 15, 2022 eruption of the Hunga volcano, the most explosive volcanic event of the satellite era. Combining unprecedented satellite, balloon, and ground-based observations with global modeling studies, the report documents the eruption’s far-reaching effects on Earth’s stratosphere, climate system, and ozone layer.December 16, 2025
GML Planetary Pulse Fall 2025
GML's quarterly newsletter returns with the Fall 2025 Planetary Pulse.December 8, 2025
GML highlights at the AGU 2025 Fall Meeting
Federal and CIRES researchers in GML are presenting several talks and posters at the 2025 Fall Meeting of the American Geophysical Union and collaborating on many more.December 3, 2025
GML completes first in-situ air sampling aboard NOAA King Air aircraft
The NOAA Global Monitoring Laboratory (GML) successfully conducted the first in-situ air sampling aboard the NOAA King Air aircraft platform during early-August test flights for the National Observations of Greenhouse gases using Aircraft Profiles (NOGAP) campaign. These flights represent a significant advancement in NOAA’s atmospheric sampling capabilities.December 2, 2025
GML’s surface radiation measurements improve NOAA’s operational weather forecast models
In a new study published in the AMS journal Monthly Weather Review, GML’s surface radiation measurements were key to helping researchers identify the source of a surface temperature bias in NOAA’s operational weather forecast models.November 24, 2025
NOAA, NASA: 2025 ozone hole is 5th smallest since 1992
Scientists with NOAA and NASA have ranked this year’s ozone hole over the Antarctic as the fifth smallest since 1992 — the year that the Montreal Protocol, a landmark international agreement to phase out ozone-depleting chemicals began to take effect. During the height of this year’s ozone depletion season from September 7 through October 13, the average extent of the 2025 ozone hole was about 7.23 million square miles (18.71 million square kilometers). The ozone hole is already breaking up nearly three weeks earlier than average over the past decade. “As predicted, we’re seeing ozone holes trending smaller in area than they were in the early 2000s,” said Paul Newman, a senior scientist at the University of Maryland system and longtime leader of NASA’s ozone research team. “They’re forming later in the season and breaking up earlier.”September 30, 2025
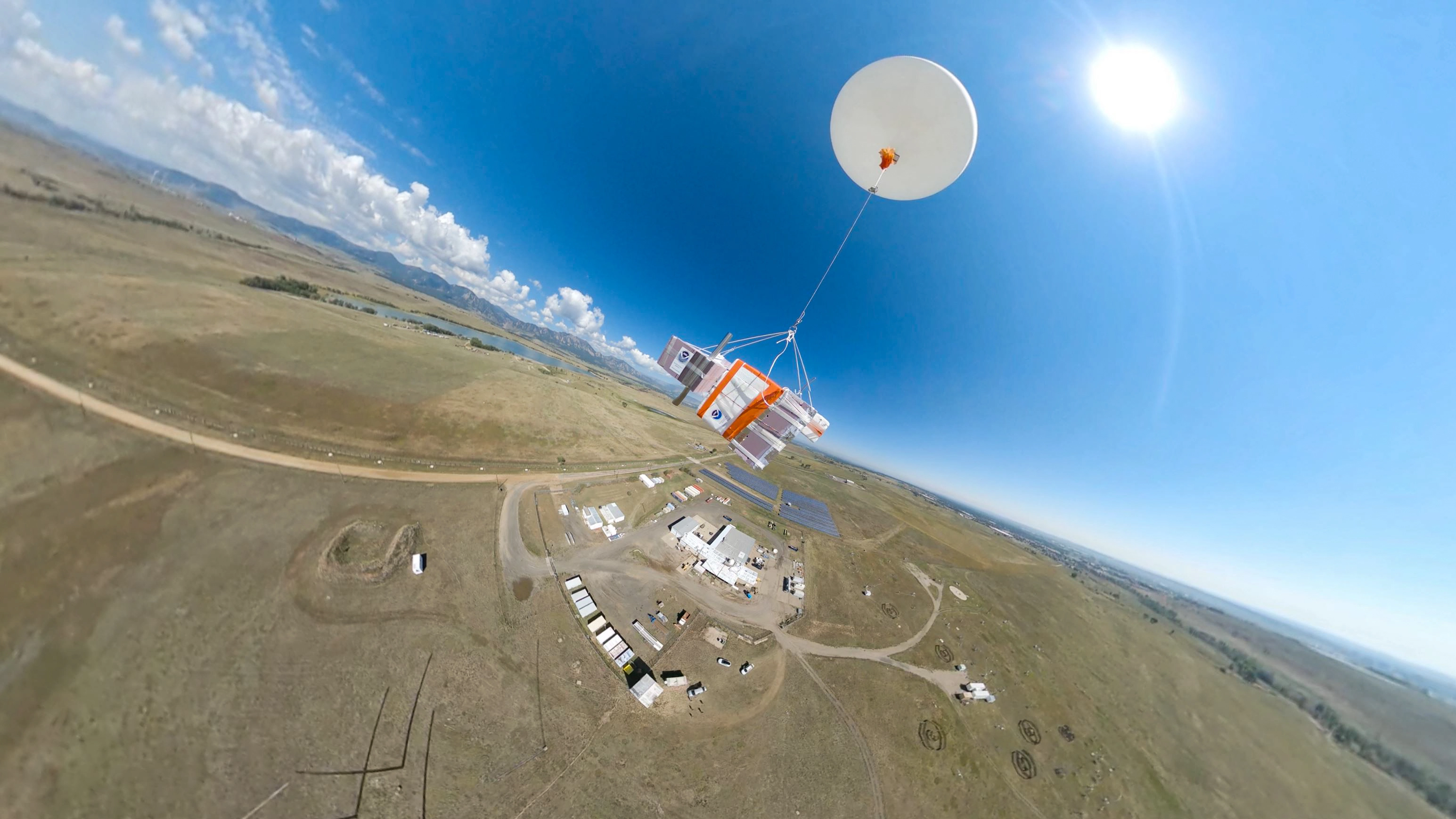
2024 Bronze Medal awarded to GML team for groundbreaking atmospheric observing platform
A team of scientists and engineers from NOAA’s Global Monitoring Laboratory has been awarded the Department of Commerce 2024 Bronze Medal for Scientific and Engineering Achievement for creating the High-altitude Operational Returning Uncrewed System (HORUS). The team is recognized “for developing a novel, low-cost, balloon-glider platform for deploying lightweight meteorological and atmospheric composition sampling and measurement systems to 90,000 feet and returning them to their original launch location.”September 29, 2025
Bronze medal awarded to research team for SABRE
A team from CSL, GML, and CPO received a DOC Bronze Medal for scientific/engineering achievement "for establishing a new paradigm for NOAA-directed stratospheric science with the successful execution of the Stratospheric Aerosol processes, Budget and Radiative Effects (SABRE) 2023 airborne science mission."September 4, 2025
New mobile NOAA Research fire weather observing facility undergoes testing in Colorado
A new, mobile fire weather observing system that can be quickly deployed to wildfire-prone regions to monitor how weather conditions contribute to fire ignition risk and behavior is undergoing testing and collecting data on a site near Boulder, Colorado. The mobile system, called “Collaborative Lower Atmospheric Mobile Profiling System” (CLAMPS), is one of several new NOAA fire weather observation systems developed during the past few years. It is a joint project between Air Resources Laboratory (ARL), Global Monitoring Laboratory (GML), Global Systems Laboratory (GSL), and Physical Sciences Laboratory (PSL), and is a key part of NOAA’s larger effort to advance our understanding of the interactions between wildfires and weather.April 2, 2025
Photo feature: Last light at South Pole brings 6 months of darkness
In the Northern Hemisphere, March 20 signals the start of spring. It's the start of fall in the Southern Hemisphere, where researchers and staff at NOAA’s South Pole Observatory recently witnessed the fading light of the sun and the start of six months of darkness.February 27, 2025
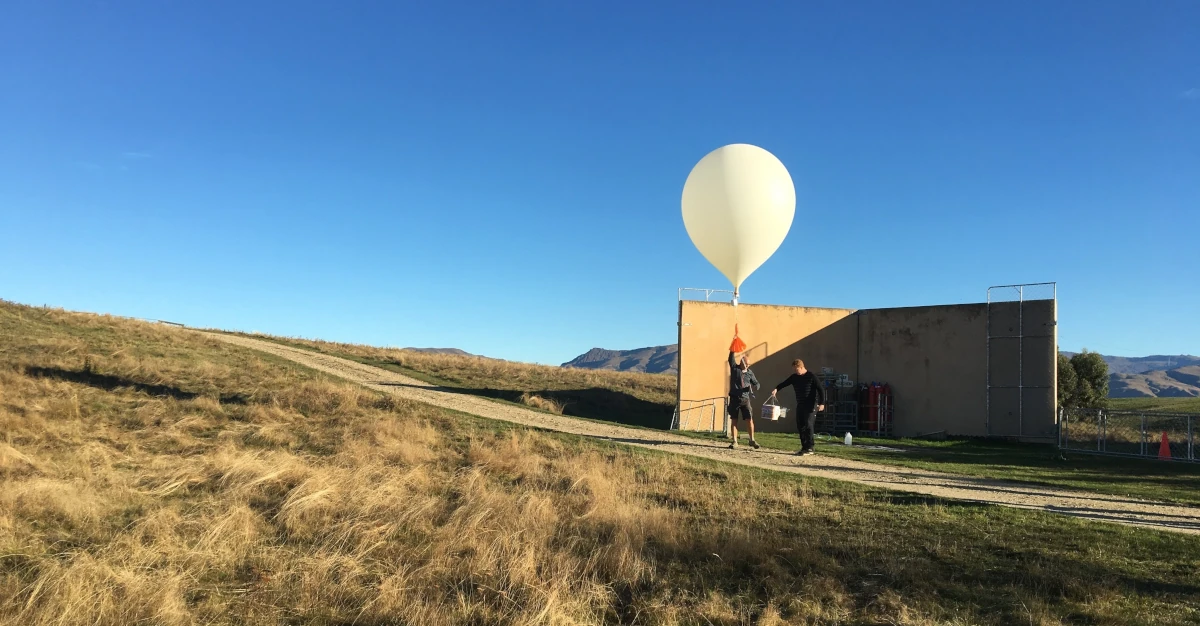
GML’s 20-year water vapor record at Lauder, New Zealand
The NOAA Global Monitoring Laboratory has reached a milestone: the longest continuous upper atmospheric water vapor record in the southern hemisphere.January 16, 2025
Biden-Harris Administration, NOAA invest $15 million to help protect Western U.S. communities from wildfire
The Department of Commerce and NOAA announced today that approximately $15 million has been provided through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law to construct and deploy a new suite of fire weather observing systems in high-risk locations in the Western United States to support wildfire prediction, detection and monitoring.