News

May 22, 2014
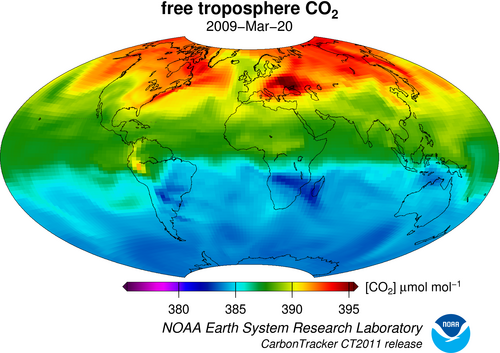
Tracking carbon dioxide across the globe
Between burning fossil fuels and clearing forests, humans emit far more carbon dioxide than Earth’s natural physical and biological processes can remove from the atmosphere. Fundamental to any attempts to understand, slow, or reverse the build up of atmospheric carbon dioxide is a global accounting of where it’s released and stored. That’s why scientists at NOAA’s Earth Systems Research Laboratory created CarbonTracker: a carbon dioxide measuring and modeling system that tracks sources and sinks around the globe.February 12, 2014
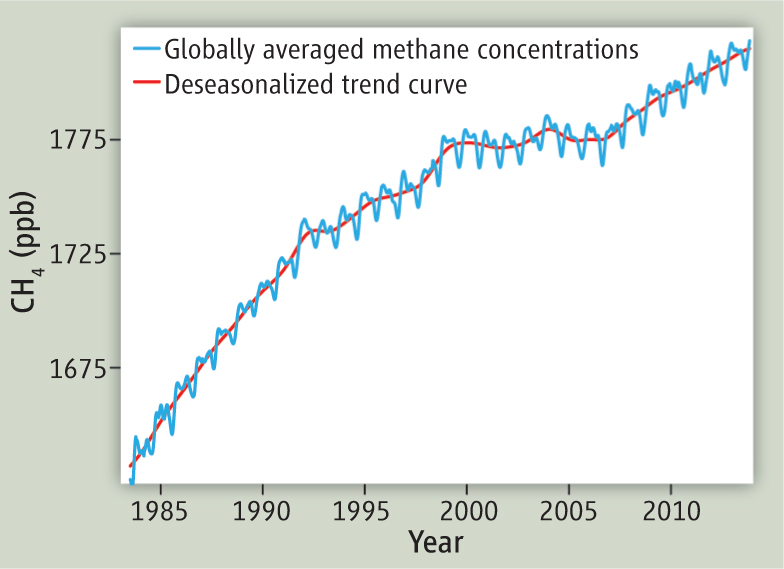
Renewed Increase in Atmospheric Methane Concentrations
In an article published in Science Perspectives, scientists from ESRL, the UK and France show that total global emissions of methane increased by 15 to 22 Tg CH4 yr-1 starting in 2007. This result is based on methane measurements from NOAA ESRL GMD’s ~70-site sampling network.February 7, 2014
Dry conditions in Amazonia reduce uptake of carbon dioxide
As climates change, the lush tropical ecosystems of the Amazon Basin may release more of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than they absorb, according to a new study published Feb. 6 in Nature.October 24, 2013
ESRL’s Pieter Tans and greenhouse gas reference network team given the 2013 Colorado Governor’s Awards for High-Impact Research.
Dr. Pieter Tans and his team of researchers at ESRL's Global Monitoring Division were honored for work in Atmospheric Sciences for the Global Greenhouse Gas Reference Network. Tans and team developed and sustained the careful and continuous collection of atmospheric observations to create a long-term record of atmospheric trace gases that is helping scientists around the globe understand the Earth system and how humans are changing the dynamics of the climate on the Earth.July 24, 2013
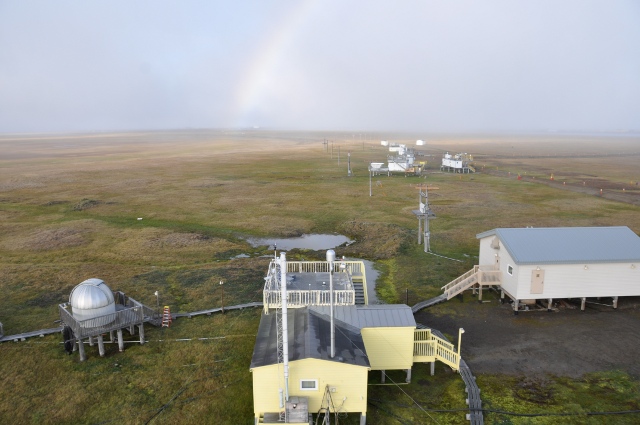
NOAA's Barrow, Alaska, Observatory marks 40 years of continuously monitoring carbon pollution in the Arctic
40 years ago, on July 24, 1973, NOAA’s atmospheric observatory in Barrow, Alaska—the U.S.’ northernmost city, located at the tip of the North Slope—began measurements of carbon dioxide pollution with a continuous analyzer, providing one of the world’s most important records of this potent heat-trapping gas.August 2, 2012
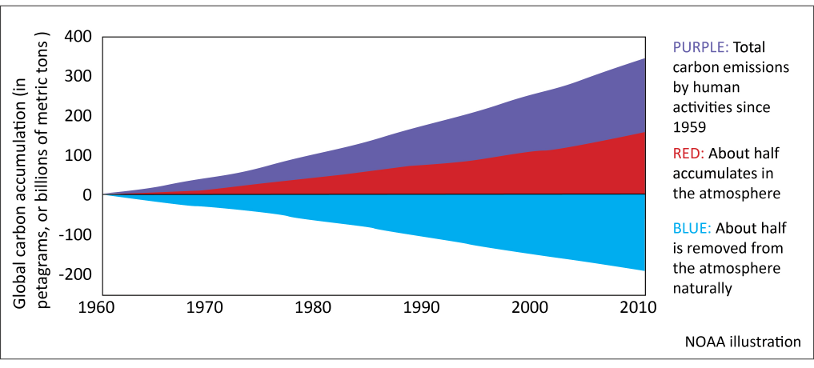
Earth's oceans and ecosystems still absorbing about half the greenhouse gases emitted by people
Earth's oceans, forests and other ecosystems continue to soak up about half the carbon dioxide emitted into the atmosphere by human activities, even as those emissions have increased, according to a study by University of Colorado and NOAA scientists.November 9, 2011
NOAA greenhouse gas index continues climbing
NOAA’s updated Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (AGGI), which measures the direct climate influence of many greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane, shows a continued steady upward trend that began with the Industrial Revolution of the 1880s.September 19, 2011
Three NOAA/ESRL AirCore samplers deployed in back-to-back balloon launches
On September 10, 2011, NOAA and CIRES scientists and engineers teamed up with the non-profit group Edge of Space Sciences (EOSS) to launch three AirCore samplers of varying sizes and material coatings. The resulting data set shows excellent agreement between the three samples for CO2, CH4, and CO, and also characterizes some regions of atmospheric variability.December 16, 2010
NOAA Scientist Awarded Revelle Medal at AGU
For his work in expanding our understanding of the global carbon cycle and raising awareness for climate change, Pieter Tans, Ph.D., was awarded the Roger Revelle Medal at the 2010 fall meeting of the American Geophysical Union in San Francisco.