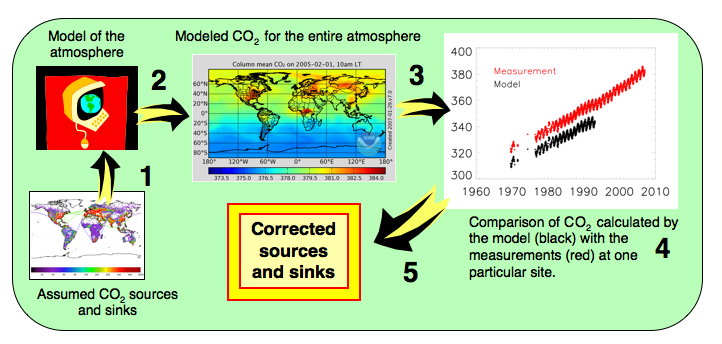
CarbonTracker integrates our current understanding of CO2 exchanges between the atmosphere and the other carbon reservoirs together with atmospheric measurements of CO2. A source adds some CO2 to the atmosphere while a sink removes some CO2 from the atmosphere.
The CarbonTracker loop starts with a "first guess" for the atmosphere sources and sinks distributed in space and time. These are fed into an atmospheric model which simulates the mixing of the air over the whole globe (step 2). At the location and time when measurements are available, the model outputs a "modeled" mole fraction of CO2 (step 3). The modeled CO2 values are then compared with the measurements themselves (step 4). Finally, a statistical model corrects the assumed CO2 sources and sinks to "best" reduce the differences between the modeled CO2 values and the measurements (step 5).