More than two years after road access and electrical power to the Mauna Loa Observatory was cut off by lava flows, NOAA staff continue to make critical measurements of the atmosphere and other environmental variables at the remote site.
In 2023, observatory staff installed solar panels at the site and resumed some measurements, including the independent carbon dioxide monitoring programs run by the Global Monitoring Laboratory and Scripps Institution of Oceanography, as well as other atmospheric measurements.
Construction of a temporary road to access the observatory site is anticipated to begin in summer 2025.
Media can contact: Theo Stein (303) 819-7409 (theo.stein@noaa.gov)
NOAA In Situ Methane (CH4) Measurements
Organization(s):
![]() National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA),
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA),
Global Monitoring Laboratory (GML)
What does this program measure?
Atmospheric methane (CH4) is measured in nanomoles per mole or nmole (abbreviated ppb).
How does this program work?
Cavity Ring-Down Spectroscopy is used in this project with the instruments, location and frequency listed below.
| Methane Instruments | Frequency | Site |
|---|---|---|
| CRDS Gas Analyzer | continuous | MLO |
| 2.5-L glass flask AIRKIT pump unit | 2 pair/week | Kumukahi |
| 2.5-L glass flasks,MAKS pump unit | 1 pair/week | MLO |
| 2.5-L evacuated glass flasks | 1 pair/week | MLO |
Why is this research important?
Methane is a greenhouse gas with a global warming potential.
Are there any trends in the data?
Methane was steadily increasing in the 1980's, it's growth rate slowed in the late 1990's, and then increased again after that.
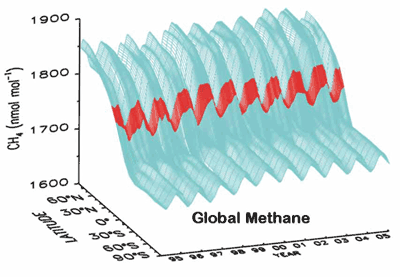
In the chart above, a three-dimensional presentation of global methane over time and latitude shows Mauna Loa data highlighted in red.
What is it's role in global climate change?
Methane produces about 15-20% of present day greenhouse gas climate forcing. Methane is prduced by fossil fuel production and agriculture.
Direct radiative forcing due to the increase in methane since pre-industrial times is ~0.5 Wm-2
The NOAA GML Carbon Cycle-Greenhouse Gases group (CCGG) conducts research to understand the global carbon cycle and its effects on climate. At CCGG measurements are made to determine baseline levels, trends and causes of variability of several atmospheric gases (carbon dioxide, methane and carbon monoxide), that have the potential to affect global climate.
To obtain detailed understanding of the short term as well as long term variations of the greenhouse gases, CCGG makes on-site measurements at the four NOAA/CMDL baseline observatories, which are far from any pollution sources affecting the gases of interest.
Comments and References
Please visit our web site at https://gml.noaa.gov/ccgg/flask.html
Dlugokencky, E J et al, Atmospheric methane at Mauna Loa and Barrow observatories: Presentation and Analysis of In-Situ Measurements. J. Geophys. Res., 100, 23,103 -23, 113, 1995.
Masarie, K A et al, A Rule-based Expert system for evaluating the quality of long-term, In Situ, Gas Chromatographic Measurements of atmospheric methane, NOAA Tech. Memo. ERL CMDL-3, NOAA Environ. Res. Lab, Boulder, Colorado, 1991.
Lead Investigator(s):
MLO Contacts(s):
Aidan Colton
808-933-6965 (x233)
Matthew.Martinsen
808-933-6965 (x228)
Web Site(s):
http://gml.noaa.gov/ccgg/flask.html
Date Started:
04-03-1987
Related Programs
In Situ Carbon Dioxide
In Situ Carbon Monoxide
Cooperative Global Air Sampling
Greenhouse Gases
